Malformation diagnosed during pregnancy
(Video: Dr. Nili Yanai)
One out of every 1,000 infants born in Israel suffers from a cleft lip, cleft palate, or both. These are congenital malformations of the face that occur due to a disruption in the fusion process of the lip and palate. What exactly is a cleft palate or lip, how are they diagnosed, and how are they treated? To answer those questions Ynet spoke with an expert on the matter.
Read more:
What is a cleft lip?
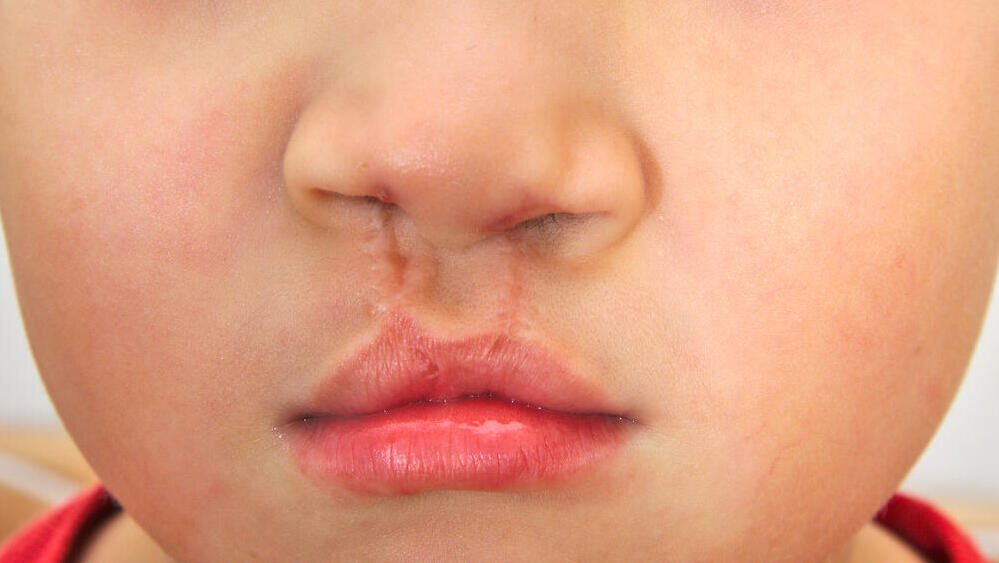
When the upper lip is not fully formed. The defect can appear as a groove in the lip or as a broader cleft that extends upwards and may involve the nose. It can occur on one side of the lip, in the center, or on both sides.
What is a cleft palate?
A split or opening in the roof of the mouth. The cleft can be in the hard part of the palate, closer to the teeth, involving the upper gum and lip, or in the soft part towards the back.
Who is at risk of having a baby with a cleft lip or cleft palate?
A congenital defect can occur as an isolated incident or as part of other congenital abnormalities. In cases where there is a history of one or more members in the extended family being born with a cleft lip, cleft palate, or a combination of both, the risk increases.
Often, the problem is part of a genetic syndrome. In such cases, there may be additional organ abnormalities, such as brain, limb, or heart defects. These may appear in the family for the first time or be inherited. Parents can be carriers of the genetic mutation without experiencing any symptoms themselves. Therefore, genetic counseling and diagnosis can be important to help identify such syndromes in advance. In most cases, the defect occurs without a family history or a genetic cause. For example, it may result from an unexplained disruption in facial development. Certain medications, such as antiepileptic drugs, can also cause the condition.
How is the condition detected, and at what stage of pregnancy?
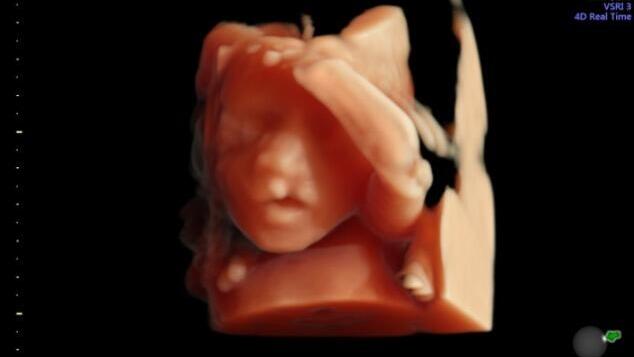
The condition can be detected through an ultrasound examination, and the more severe the defect, the earlier its detection is possible. In severe cases, it can be detected as early as weeks 13-14 of pregnancy. If it is a cleft lip only, it is usually detected during the routine fetal anatomy scan performed around weeks 20-24. A cleft palate alone is generally not detectable during pregnancy because the facial bones hide the palate, making it difficult to assess its completeness. Outer transparency examinations performed around weeks 11-13 can alert to the risk of finding abnormalities in the fetus, so a woman at risk would know if she needs to undergo a more detailed assessment to diagnose the defect.
What is the percentage of misdiagnosis?
False positive diagnosis, meaning suspecting the presence of a cleft defect when the fetus is actually healthy, occurs rarely, and the error is usually detected in further tests. False negative diagnosis is more frequent: the defect exists, but it was not diagnosed in the ultrasound examination. There are cases where the defect is only detected at a later stage of pregnancy. Sometimes, during early fetal anatomy scans performed around weeks 14-16, doctors may miss the defect, while in later scans, they usually diagnose it.
Is it considered a high-risk pregnancy?
No. A high-risk pregnancy is a condition that requires close monitoring and treatment to prevent complications for both the mother and the fetus, and this is not the case here. If a cleft lip or cleft palate is detected, genetic counseling is necessary, but there is no need for intensive monitoring or medical treatment, and the woman is not required to enter a high-risk pregnancy care unit.
How is treatment conducted upon the detection of a defect?
In such cases, pregnancy is managed by a team that includes geneticists, specialized cleft surgeons, plastic surgeons, neonatologists, pediatricians, and other experts. After the diagnosis, a consultation with parents will be held, to present the complete examination of prenatal testing, the implications of the defect, and the postnatal treatment of the child. In some cases, it may involve a severe genetic syndrome, and the option of terminating the pregnancy would be discussed. Some people may not be able to cope with a defect that requires a series of surgeries and a lengthy rehabilitation process, although in most cases, the defects can be treated optimally.
Providing support to the parents during and after pregnancy is an integral part of the treatment. Volunteers from "Sfat Halev" a non-profit NGO accompany families dealing with cleft lip and cleft palate from the prenatal stage through adulthood. The majority of the association's volunteers are mothers of children with such defects.