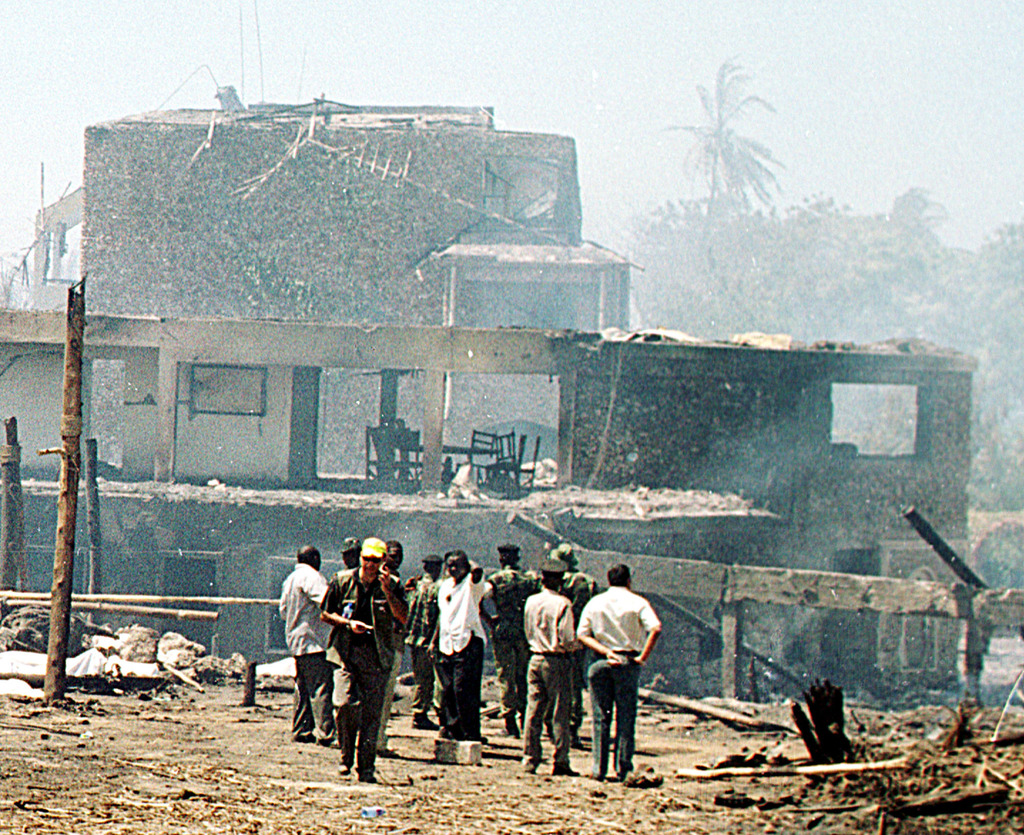
Al Qaeda’s second-in-command, accused of helping to mastermind the 1998 bombings of two U.S. embassies in Africa, was killed in Iran in August by Israeli operatives acting at the behest of the United States, the New York Times reported on Friday, citing intelligence officials.
Abdullah Ahmed Abdullah, who went by the nom de guerre Abu Muhammad al-Masri, was gunned down by two men on a motorcycle in the streets of Tehran on Aug. 7, the Times reported.
The killing of Masri, who was seen as a likely successor to al Qaeda’s current leader, Ayman al-Zawahiri, was kept secret until now, the newspaper said.
It was unclear what, if any, role the United States had in the killing of the Egyptian-born militant, the Times said. U.S. authorities had been tracking Masri and other al Qaeda operatives in Iran for years, it said.
Al Qaeda has not announced his death, Iranian officials have covered it up and no government has publicly claimed responsibility, the Times said.
A U.S. official, speaking to Reuters on condition of anonymity, declined to confirm any details of the Times’ story or say whether there was any U.S. involvement. The White House National Security Council did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
3 View gallery
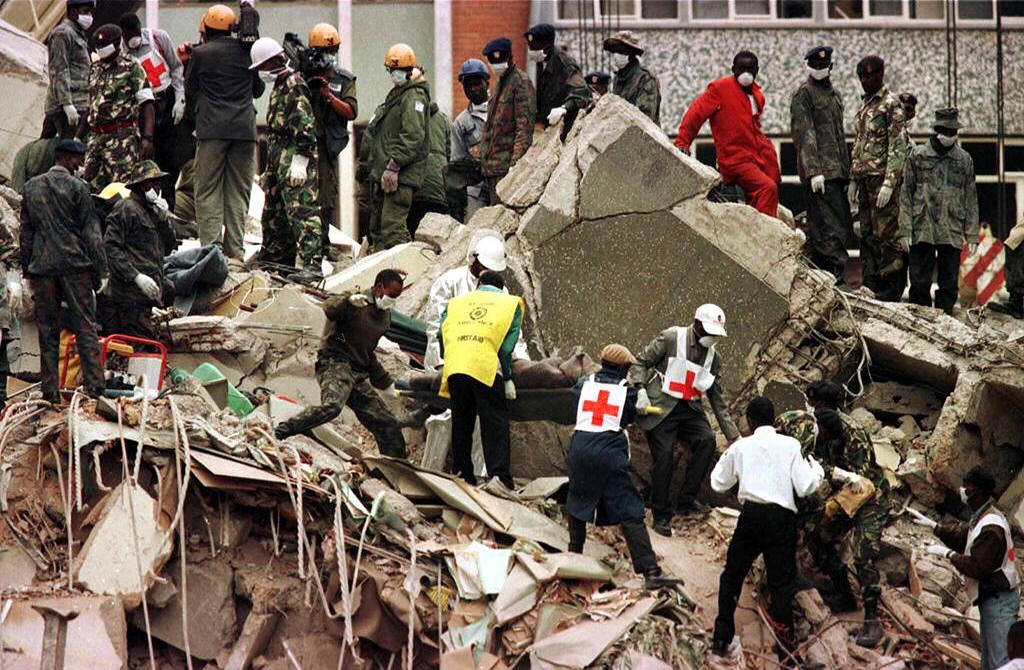


The aftermath of the 1998 bombing of the American Embassy in Nairobi, Kenya
(Photo: AFP)
Masri, one of al Qaeda’s founding leaders, was killed along with his daughter, the widow of former al Qaeda chief Osama bin Laden’s son, Hamza bin Laden, the Times reported.
Osama bin Laden orchestrated the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks on the United States and was killed in a U.S. raid in Pakistan in 2011.
Shi’ite Iran and al Qaeda, a Sunni Muslim militant organization, have long been enemies.
Iran denied the report, saying in a statement that there were no al Qaeda "terrorists" on Iranian soil.
"From time to time, Washington and Tel Aviv try to tie Iran to such groups by lying and leaking false information to the media in order to avoid responsibility for the criminal activities of this group and other terrorist groups in the region," the Iranian Foreign Ministry said.
Masri had been in Iran’s “custody” since 2003 but had been living freely in an upscale suburb of Tehran since 2015, the Times cited unnamed U.S. intelligence officials as saying.
U.S. counterterrorism officials believe Iran, also a U.S. enemy, may have let them live there to conduct operations against U.S. targets, the Times said.
It was not immediately known what, if any, impact Masri’s death has had on al Qaeda’s activities. Even as it has lost senior leaders in the nearly two decades since the attacks on New York and Washington, it has maintained active affiliates from the Middle East to Afghanistan to West Africa.
First published: 09:13, 11.14.20