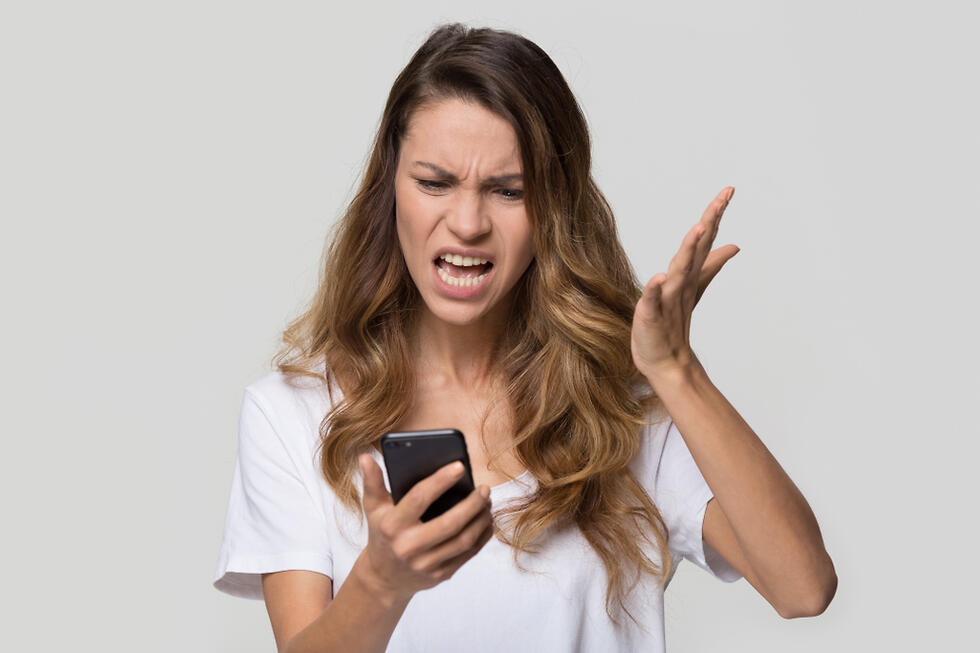
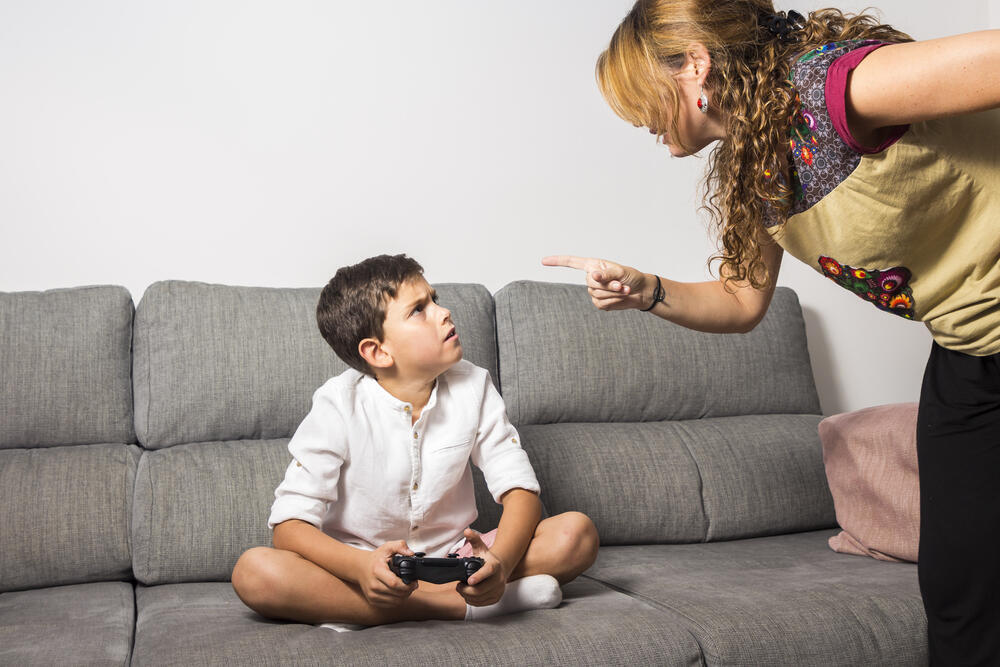
Irritability is an intense emotional reaction that develops when anger becomes prolonged and persistent. While anger is a natural and often temporary emotion that arises in response to specific events, such as frustration or perceived injustice, irritability represents a shift into a more enduring pattern. It can manifest even in response to minor or trivial matters, becoming a constant presence that does not easily dissipate. This persistent state of emotional tension can have significant negative effects on various aspects of life, including physical health, interpersonal relationships, and overall emotional well-being.
Health impacts of irritability
Unaddressed irritability can have serious and far-reaching consequences on physical health. Without appropriate intervention, these effects tend to worsen over time. Some of the most common health impacts associated with chronic irritability include:
- Cardiovascular Issues: Prolonged irritability elevates blood pressure levels, increasing the risk of heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes.
- Weakened Immune System: Chronic anger and irritability can suppress immune function, leaving the body more vulnerable to infections and illnesses.
- Digestive Disorders: Persistent frustration and emotional tension can result in gastrointestinal problems such as stomach pain, gastritis, and other digestive system disturbances.
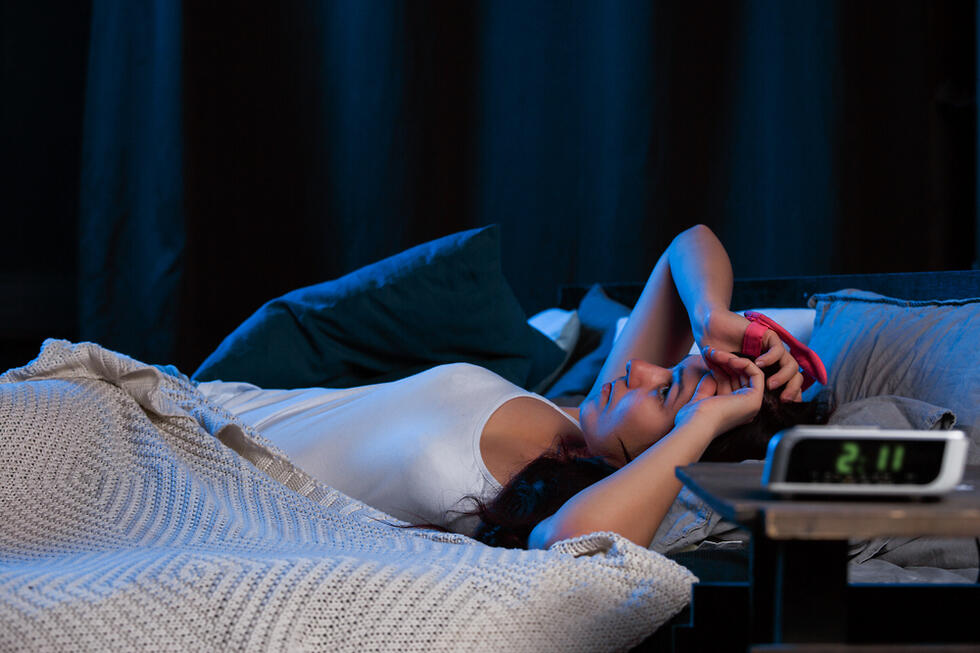
- Sleep Problems: Irritability can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to chronic fatigue, reduced energy levels, and impaired daily functioning.
- Accelerated Aging: Chronic stress and anger are associated with an acceleration of aging processes, as prolonged emotional tension impacts the body on multiple levels.
The dual nature of anger
It is important to distinguish between anger and irritability. While anger is often perceived as a negative emotion, it can serve a functional purpose when expressed constructively. Anger can act as a signal, alerting us to unmet needs or injustices. When channeled positively, anger can be a powerful motivator for action and change. It can help us defend ourselves, set healthy boundaries, and advocate for our rights. However, when anger becomes chronic and transforms into irritability, it ceases to be productive and instead becomes harmful, undermining both mental and physical health.
Get the Ynetnews app on your smartphone: Google Play: https://bit.ly/4eJ37pE | Apple App Store: https://bit.ly/3ZL7iNv
Strategies for managing irritability
To mitigate the harmful effects of irritability and maintain mental and physical well-being, it is important to develop effective coping strategies. Below are several approaches that can help manage and reduce irritability:
- Identify Triggers: Understanding the underlying causes of irritability is the first step in addressing it. Keeping an emotional journal can help track patterns, identify triggers, and develop strategies for prevention.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Activities such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help calm both the mind and body, reducing emotional tension.
- Adopt Positive Thinking Patterns: Shifting focus from problems to solutions and reframing negative thoughts can help interrupt cycles of irritability. Cognitive-behavioral techniques are particularly effective in preventing the development of negative thought patterns.
- Engage in Physical Activity: Regular exercise is a proven stress reliever. Physical activity not only reduces stress levels but also releases endorphins, which improve mood and promote emotional balance.
- Prioritize Quality Sleep: Adequate and restorative sleep is essential for maintaining both mental and physical health. Establishing a consistent sleep routine can significantly reduce irritability.
- Address Physiological Factors: Research suggests that irritability may have physiological causes, such as imbalances in blood sugar levels. Ensuring proper nutrition and maintaining balanced blood sugar levels can play a critical role in managing chronic irritability.
Final thoughts
By understanding the triggers and physiological underpinnings of irritability, individuals can take proactive steps to manage this emotion and prevent it from interfering with their lives. Incorporating relaxation techniques, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking professional support when needed can help reduce the impact of irritability and foster emotional resilience.