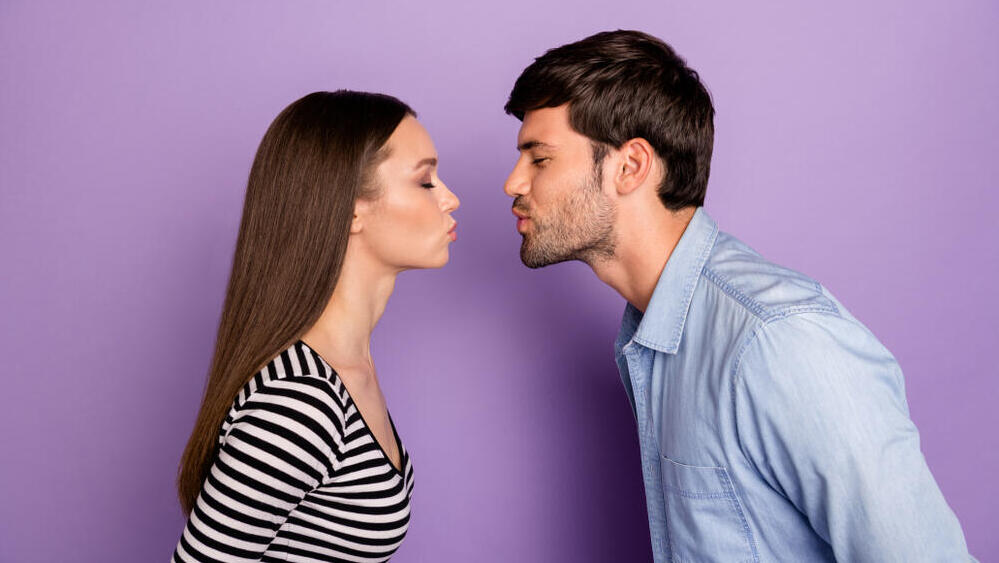
A new study suggests that people with celiac disease can kiss someone who has consumed gluten without significant risk of exposure, and in many cases, without taking special precautions.
Researchers from Columbia and Stanford Universities found that in most instances, the amount of gluten transferred during a kiss — even after eating gluten-rich crackers — was far below the threshold needed to trigger a reaction in celiac patients.
The study, presented this week at Digestive Disease Week 2025 in San Diego, aimed to answer a question many people with celiac disease have long wondered: Can kissing someone who has eaten gluten be harmful? Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder where the body reacts to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye.
"I’m asked about this all the time," said Dr. Nilsen Fernandez-Baker, director of the celiac program at Stanford University. "Until now, no scientific study had addressed this directly. We’ve all relied on personal judgment."
Dr. Ann Lee, the study’s lead researcher from Columbia University, added, “Many people told us they ask their partner to brush their teeth or use mouthwash before kissing. This creates anxiety around dating and affects quality of life — we wanted to investigate this scientifically.”
Dr. Nadav Ilani, a gastroenterologist at Clalit Health Services in Jerusalem, noted, “This research could help ease concerns for celiac patients worried about gluten exposure through kissing. While no medications are currently available in Israel that allow patients to safely consume gluten, future treatments may make this possible.”
The study involved 10 couples, with one partner diagnosed with celiac disease. The healthy partner ate 10 gluten-containing crackers before kissing their celiac partner. In one scenario, the couples waited five minutes before engaging in a one-minute French kiss. In another, the healthy partner drank half a glass of water immediately after eating the crackers, before kissing.
After each kiss, saliva samples from the celiac patient were tested for gluten, and urine samples were also analyzed. Only two instances showed gluten levels exceeding 20 parts per million — the threshold considered "gluten-free" in food. One sample showed a high level of 154 parts per million and a positive urine test, though the patient showed no symptoms. In both cases, the healthy partner did not drink water before the kiss. When water was consumed before kissing, no gluten was detected.
Dr. Ilani emphasized that the researchers used extreme conditions for the study. "The participants ate 10 gluten-rich crackers and then kissed for at least a minute. This doesn't simulate a typical situation — most people don’t consume this much gluten in one meal," he said. "Therefore, if even in these extreme conditions exposure was minimal, it's likely that in everyday situations, the risk is even lower."
However, Dr. Ilani also cautioned that the study had limitations. “It involved a small sample size of just 10 couples. If hundreds or thousands of patients were tested, we might find some who are sensitive to even smaller amounts of gluten. Also, the reactions to gluten aren’t always immediate, and in this study, saliva was tested right after the kiss, so some possible reactions might not have been detected.”
<< Get the Ynetnews app on your smartphone: Google Play: https://bit.ly/4eJ37pE | Apple App Store: https://bit.ly/3ZL7iNv >>
Celiac disease is an autoimmune condition that affects about 1% of the population and can cause serious health problems if gluten is consumed. Dr. Ilani explained that the disease can be fully managed through a strict gluten-free diet. "Oats contain a different type of gluten, which typically doesn’t provoke a reaction in most patients. When individuals avoid gluten completely, they are considered healthy, but they must maintain a strict lifestyle," he said.
Dr. Ilani added that sensitivity to gluten can vary greatly among celiac patients. "Some people are very sensitive, while others report no symptoms even when eating small amounts of gluten," he said.