A joint effort between Israel’s National Cyber Directorate and a local startup recently thwarted a wave of phishing attempts targeting official government and security websites, an attack that could have caused severe damage to citizens and national security.
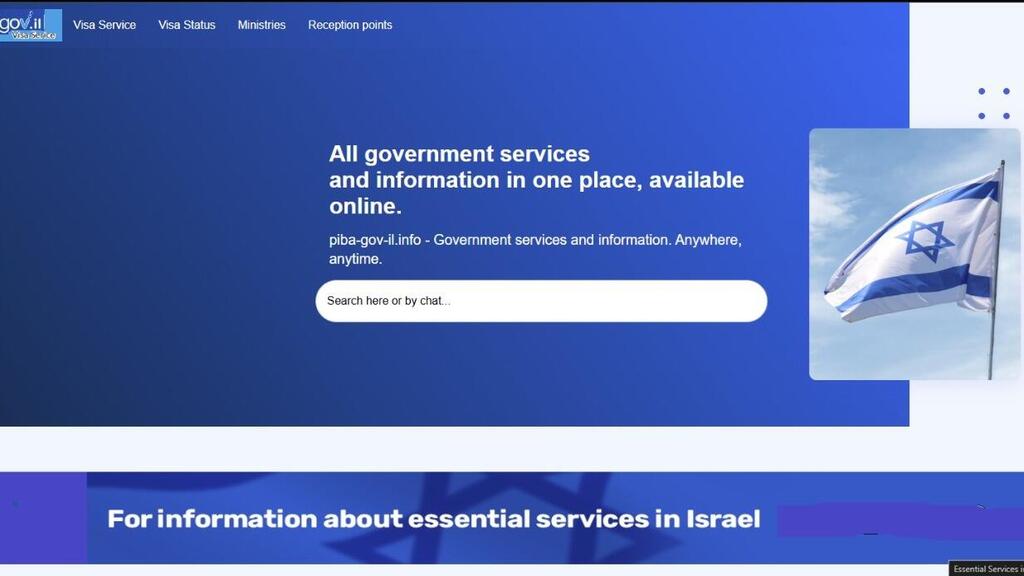
According to reports received by Ynet, the Israeli startup Malmanta AI, which specializes in early detection of attack infrastructure, uncovered dozens of fraudulent websites that closely mimicked official domains, including gov.il, the Foreign Ministry, the Mossad and even the National Cyber Directorate itself.
The sites, detected in their early stages of setup, were intended for a range of malicious purposes—from phishing and theft of financial and personal data to spreading malware and disinformation. The attempted attack was reported to the National Cyber Directorate, which led a swift takedown operation. Authorities cautioned, however, that it is not certain all of the fake domains were eliminated.
A new defense line: Proactive cyber intelligence
The incident highlights the shift in cyber defense from reactive measures to proactive intelligence. Instead of waiting for an attack to unfold and dealing with the damage, companies like Malmanta AI identify threats before they materialize.
This is made possible through advanced artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies that detect suspicious online patterns, such as domains resembling existing sites, use of unfamiliar servers, or newly built websites with content mimicking official institutions.
Such proactive defense marks a significant leap in cybersecurity. Malmanta AI’s capabilities are comparable to those of global firms like Cloudflare and Akamai, which provide proactive protection based on large-scale internet data collection and AI-driven threat analysis. Unlike those companies, Malmanta AI specializes in identifying and neutralizing local attacks relevant to Israeli institutions, giving it a strategic advantage.
Phishing as a tool of hybrid warfare
The case in Israel reflects a global trend: phishing has become a central weapon in hybrid warfare. According to international media outlets such as Politico in the U.S. and Der Spiegel in Germany, phishing campaigns against governments and militaries are increasingly common, often carried out by hostile states or terrorist groups.
The aim is not only to steal information but also to spread disinformation, undermine public trust in government institutions, and open gateways to more sophisticated cyberattacks. European governments have reported widespread phishing campaigns throughout the war in Ukraine, including sites impersonating refugee aid portals to steal personal data. In China, reports point to fake government websites used to extract business and political intelligence. Israelis have also faced repeated phishing attempts since the October 7, 2023, Hamas-led assault.
Public guidelines: how to avoid phishing attacks
The National Cyber Directorate emphasized the importance of public awareness. While advanced defense systems are constantly operating in the background, the first and most important layer of protection remains the vigilance of individual users.
Authorities urge citizens to always verify a site’s address before entering sensitive information, making sure it ends with gov.il. Users should avoid clicking suspicious links in emails or text messages and instead type official addresses directly into the browser. Warning signs such as spelling errors, odd phrasing, or mismatched design elements should also raise red flags.
Phishing techniques have become dramatically more sophisticated in recent years. What once were clumsy emails with obvious typos are now nearly indistinguishable fake websites, leveraging advanced graphics and technology to deceive the public.