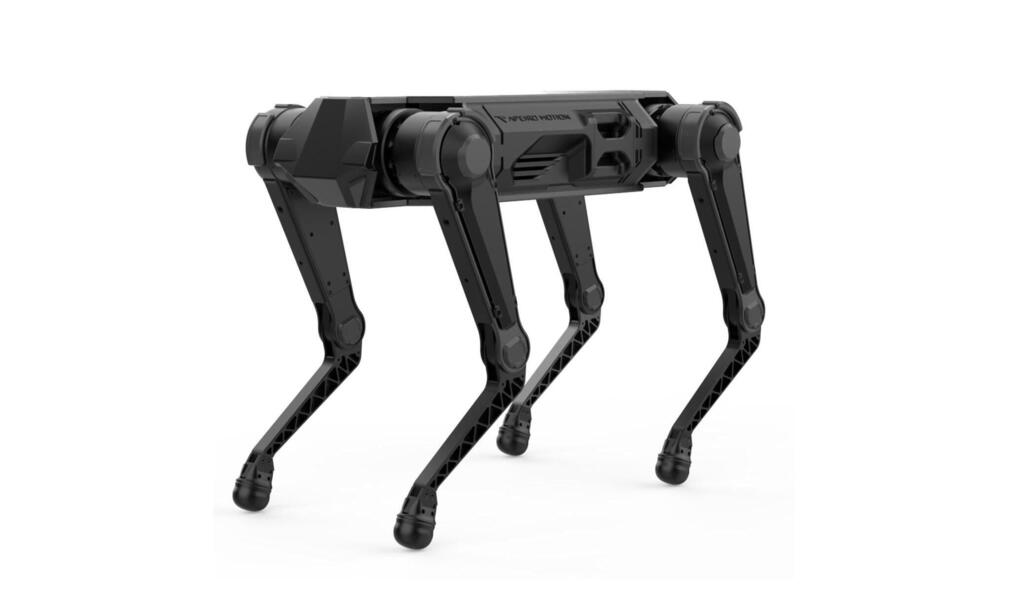
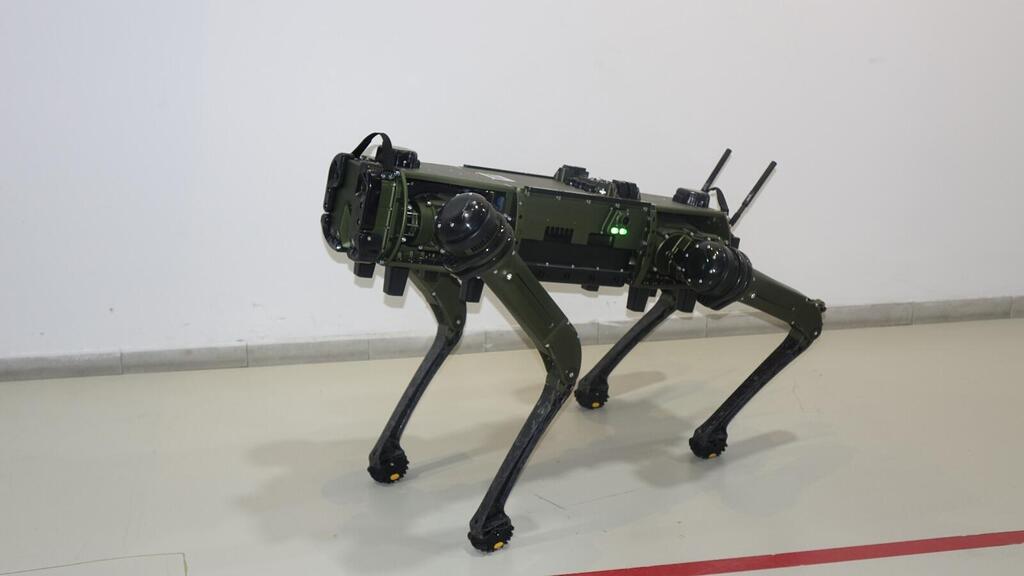
It doesn’t have a name yet, but it does have a color: blue and white. Developed in Israel, this robotic dog comes equipped with advanced tracking, navigation and voice-command capabilities. Its mission is to assist workers in the field or soldiers on the battlefield.
Fully autonomous and requiring no remote control, the robot is built to handle complex terrain such as obstacles and staircases. It’s designed to operate as part of a human team — whether that’s advancing alongside an infantry unit or supporting a commercial workforce with physically demanding tasks.
Netzer Hertz, deputy CEO of Apeiro Motion, the company behind the development based in Kochav Yair, says the idea for the robot emerged during reserve duty. “Autonomous robots are capable of completing tasks in difficult environments, and the demand for this kind of solution is only growing,” he explains.
“Organizations in both the defense and civilian sectors are searching for man’s best friend — in robotic form — to function as a team member, not a replacement and to operate in places humans cannot. Understandably, there’s a preference for robotic dogs developed in Western countries.”
Don’t underestimate the robots
The development of the robotic dog is just one initiative within the HRI consortium, a national program advancing “human-robot interaction” technologies. Established in 2022 with a budget of 57 million shekels ($15.5 million), the consortium is funded by the Israel Innovation Authority and led by Elbit Systems’ Cyber and C4I Division. This week, the consortium held its concluding conference at Reichman University, where several of its cutting-edge robotic innovations were showcased.
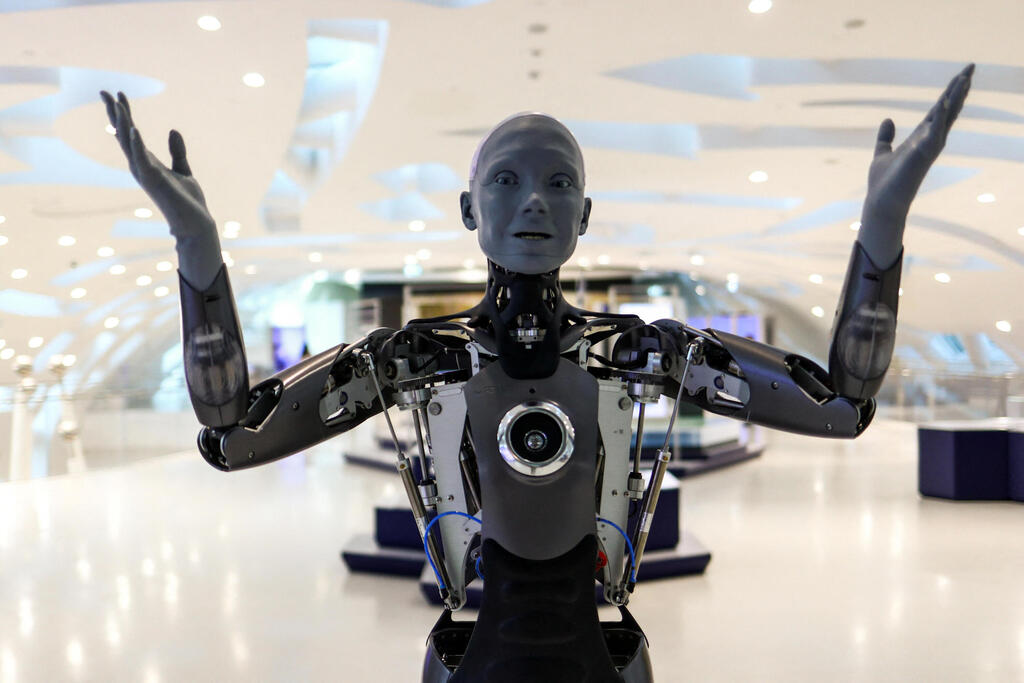
Among them was Alice, a smart, cart-like office assistant developed by Cogniteam. Despite her modest appearance, Alice could become the office’s star employee: she adapts to changing environments, performs tasks efficiently and navigates autonomously. Beyond technical skills, she also reads social cues and responds accordingly—adjusting her tone depending on whether she’s entering the CEO’s office or hanging out at the coffee corner. Alice is even programmed to push back against rude commands; if she senses disrespect, she may refuse to carry out the task.
These advanced capabilities—including the interpretation of both verbal and visual cues, analysis of social context and dynamic adjustment of behavior—allow the robot to tailor its level of autonomy, interact naturally with humans and learn from experience, much like people develop personalities and social dynamics over time.
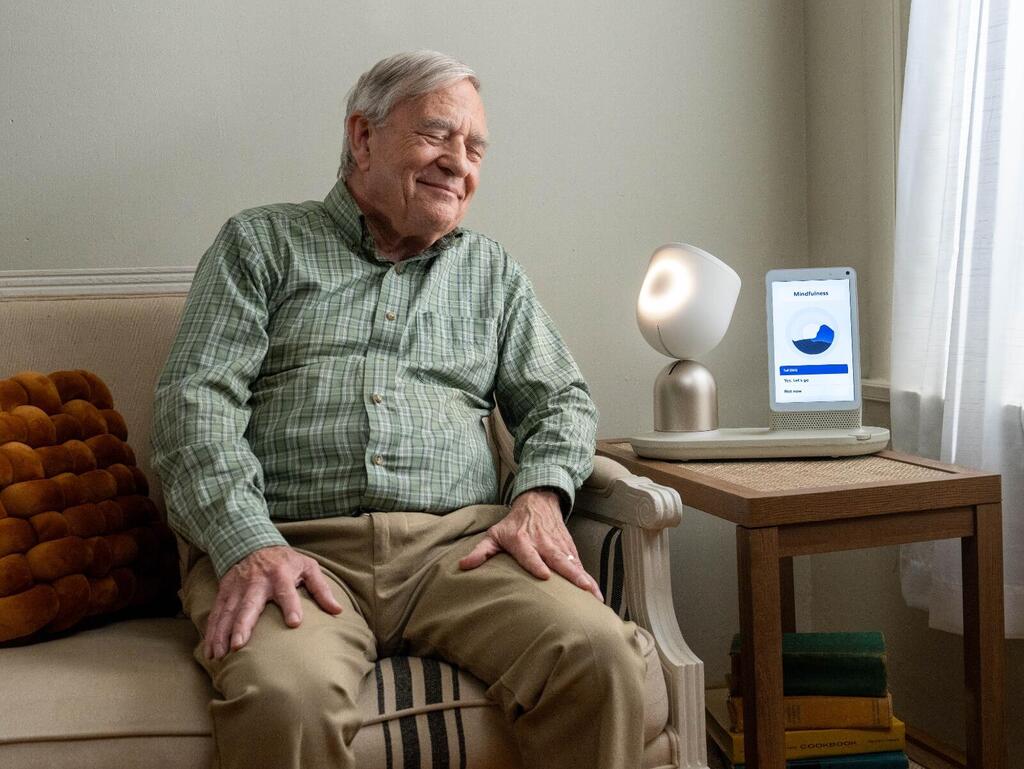
Another standout is ElliQ, a robotic companion for the elderly, developed by Intuition Robotics. Designed to alleviate loneliness, ElliQ is a self-learning assistant that adapts to individual users. She can track health routines—reminding seniors to take medication or attend physical therapy—and provides companionship through human-like gestures and responsive dialogue.
While ElliQ intentionally does not resemble a person, to avoid confusion among older users, she can tilt her head while listening to stories and respond based on emotional context and familiarity. She even plays games preferred by seniors, offering both entertainment and emotional support.
Goal: Advancing natural communication between humans and robots
One of the key insights emerging from the HRI consortium is that the rapid evolution of artificial intelligence and large language models (LLMs) is significantly enhancing robots’ ability to engage in natural communication and spatial understanding. These advancements are expected to drive a major leap in human-robot interaction (HRI), enabling robots to understand simple spoken instructions and respond optimally to changing conditions in complex environments.
One area of focus in the consortium’s work has been developing technologies to reduce people’s discomfort with using robots in shared tasks. Robots that cannot adapt to their surroundings may be perceived as threatening or intimidating. Researchers worked on tailoring the technology to human behavioral norms, incorporating natural speech capabilities, dynamic environmental learning and adaptive decision-making. These improvements enable robots to collaborate on tasks, explain actions and respond flexibly to real-world scenarios.
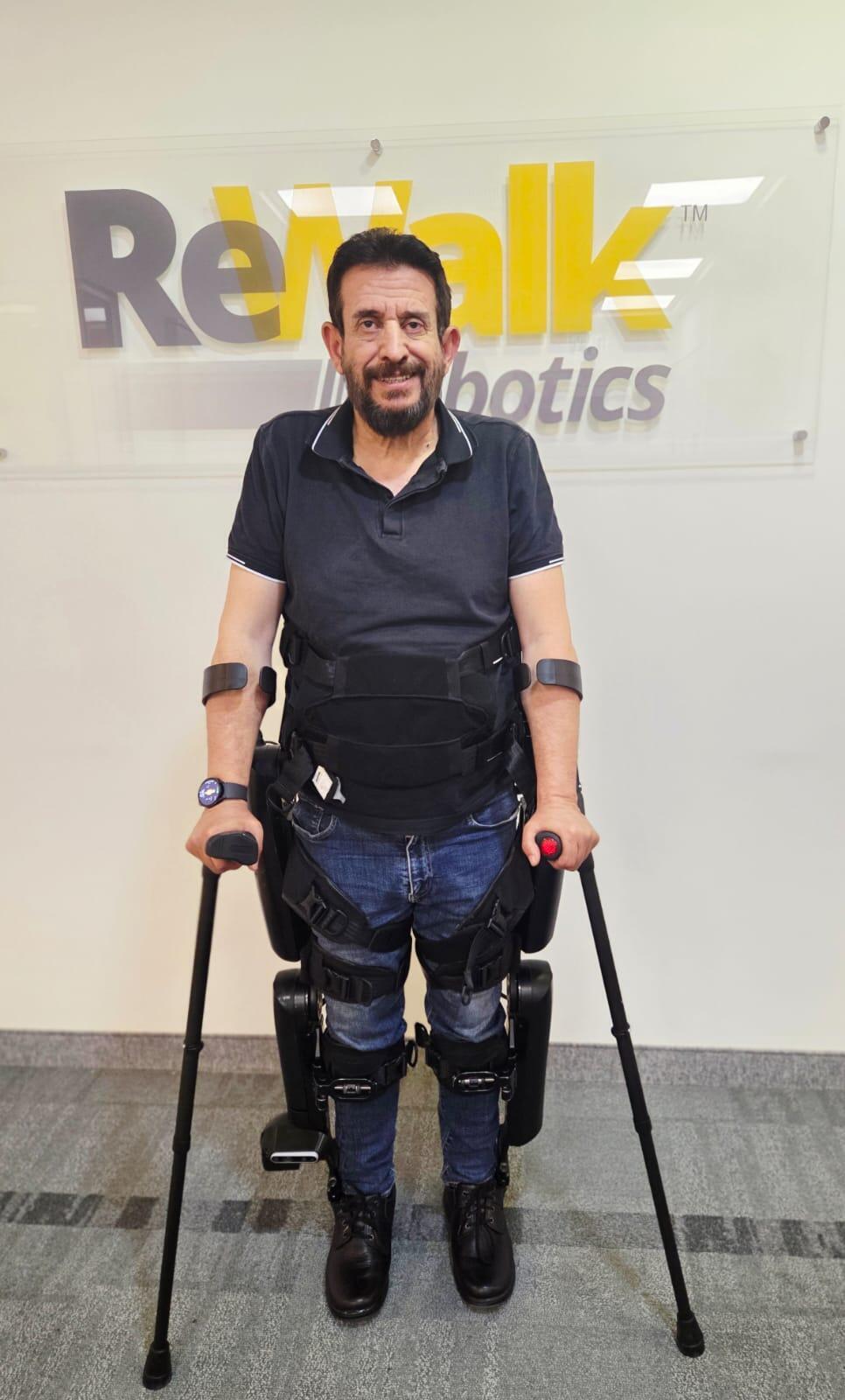
Among the technologies presented at this week’s closing conference was a new exoskeleton from Israeli firm Lifeward. Called ReWalk, the robotic suit is designed to assist people with lower limb disabilities in walking. The bionic system integrates computer vision and AI sensors that continuously collect data on position, speed and distance, allowing the exoskeleton—and the person wearing it—to move in sync with their intent. It adapts to environmental conditions and user intentions, making movement feel intuitive and helping IDF veterans and individuals with disabilities to stand, walk and navigate stairs and curbs.
Get the Ynetnews app on your smartphone: Google Play: https://bit.ly/4eJ37pE | Apple App Store: https://bit.ly/3ZL7iNv
Also featured was a robotic dog called V60 from Robotican, enhanced with an aerial twist: a drone known as Tarnegol (Hebrew for Rooster). The innovative hybrid system allows the drone to launch and land directly on the dog’s back, enabling seamless operation in challenging terrain and expanding operational range. The integration combines enhanced ground mobility with agile aerial reconnaissance, offering solutions for missions such as surveillance, rescue, security and intelligence gathering.
In a conversation with Ynet, Yossi Cohen, CTO of Elbit Systems’ Cyber and C4I Division, explained: “The consortium’s work enabled, for the first time, the integration of social capabilities alongside the impressive motor functions already available in today’s robotic platforms. It gives Israeli industry a commercial edge in developing advanced tools for hybrid task teams—humans and robots—working together across logistics, medical and homeland security fields.”
Israel Innovation Authority Chairman Dr. Alon Stopel added, “The robotics sector as developed under the HRI consortium is a prime example of a technology engine, creating opportunities for Israel to become a global leader. The Innovation Authority’s consortiums are key drivers of both technological advancement and the Israeli economy. High-tech is our natural resource, and the challenge now is to continue steering this aircraft carrier forward, so it remains a central growth engine for the Israeli economy.”