Garcinia (Garcinia cambogia) is a small tropical fruit that resembles a miniature pumpkin and grows mainly in South India and Southeast Asia.
According to clinical studies and Western medicine, scientific interest in garcinia centers on an active acid found in the fruit’s rind, hydroxycitric acid, though research results are not conclusive.
1 View gallery
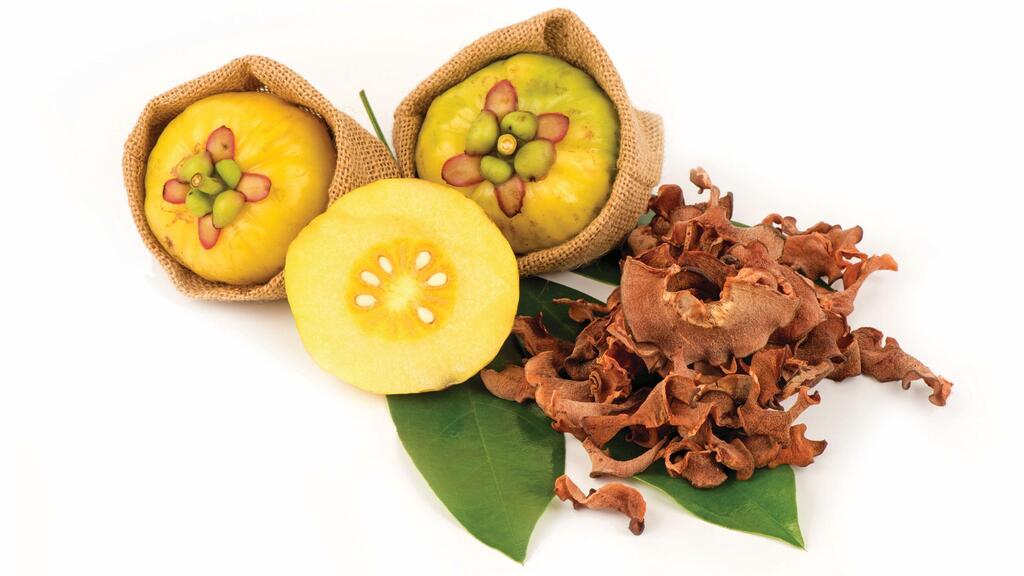


Garcinia; grows mainly in South India and Southeast Asia
(Photo: Shutterstock/ASAP Creative)
Some studies suggest that garcinia may:
• Reduce appetite by increasing serotonin levels in the brain
• Inhibit the conversion of carbohydrates into fat in the liver by blocking the enzyme ATP citrate lyase
• Support balanced blood sugar and lipid levels in cases of prediabetes or excess weight
In traditional medicine:
In Sri Lanka and India, garcinia is considered a cooling plant that aids digestion and helps cleanse the digestive system of fats and excess heat. In Ayurvedic medicine, it is also used to treat nausea and obesity and at times to help balance mood, attributed to the acid found in the fruit’s rind.
How to use it:
• Dried fruit: Used as a sour spice in fish dishes, curries and sauces to support digestion
• Powder: Can be added to smoothies or warm water before meals, though its sour taste requires getting used to
• Capsules: 500–1,000 mg before main meals, up to three times a day
Caution!
• Not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women
• May cause gas or nausea
• In high doses, or when combined with antidepressants (SSRIs), garcinia may affect serotonin levels. Consult a physician.
Note: When taking herbal remedies, consult your doctor to ensure they do not interfere with other medications or medical conditions.
The author is a clinical dietitian and herbal medicine practitioner.